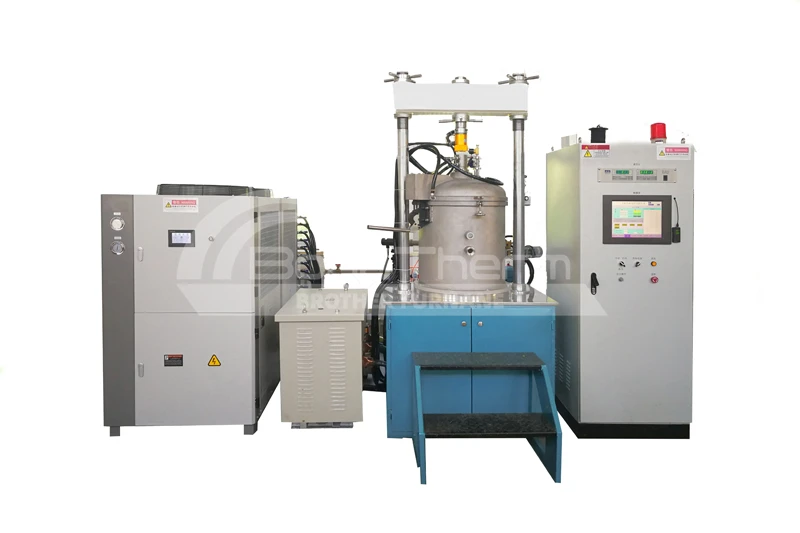
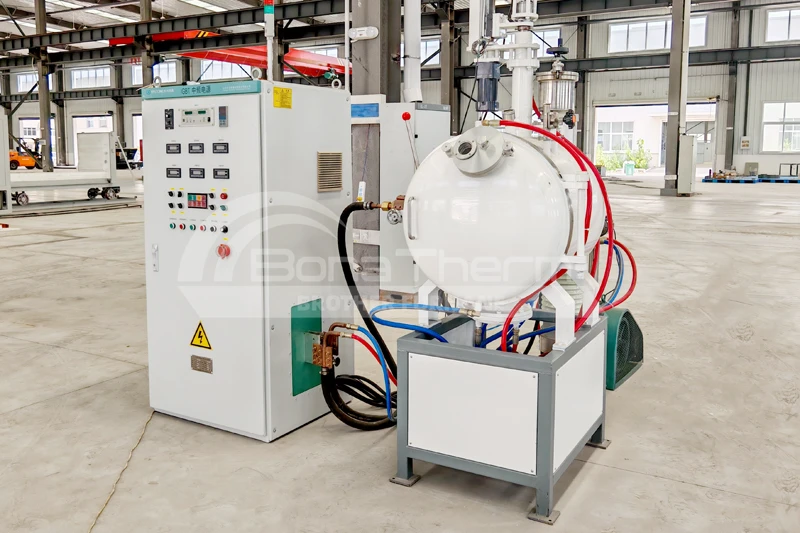
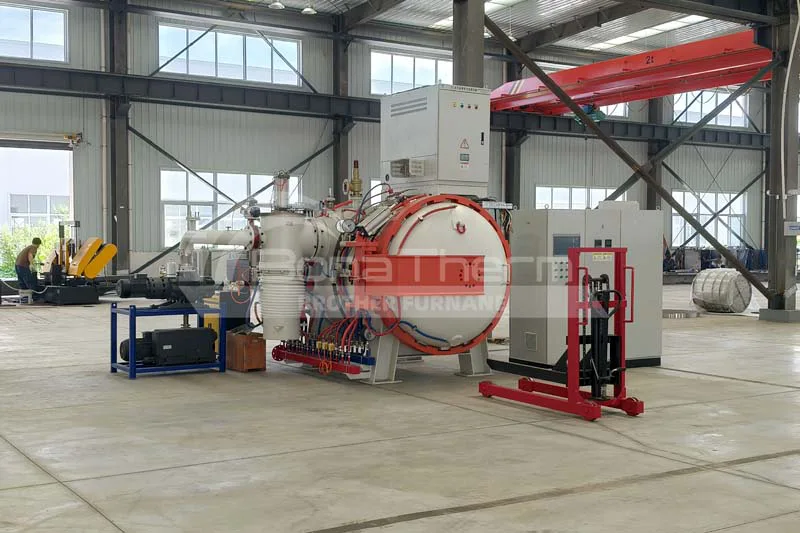
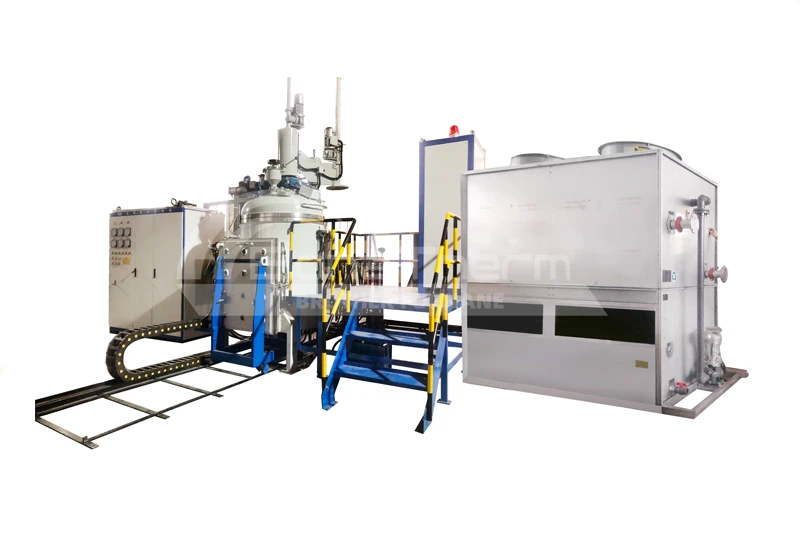
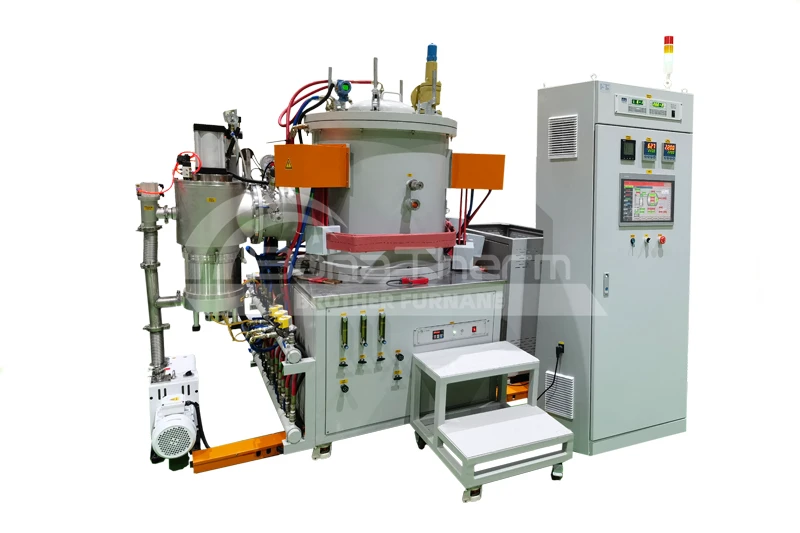
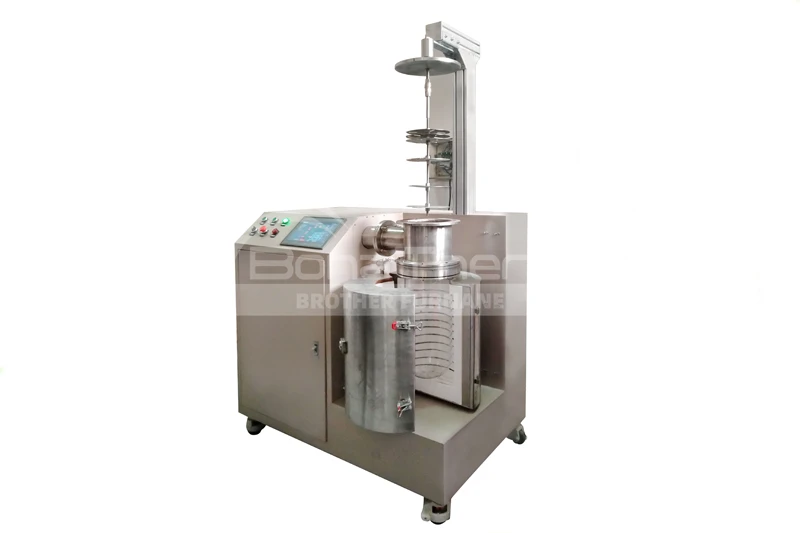
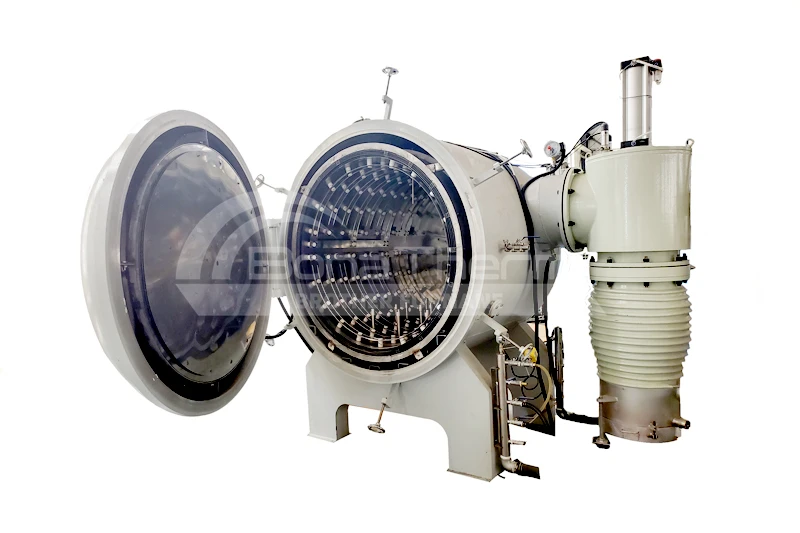
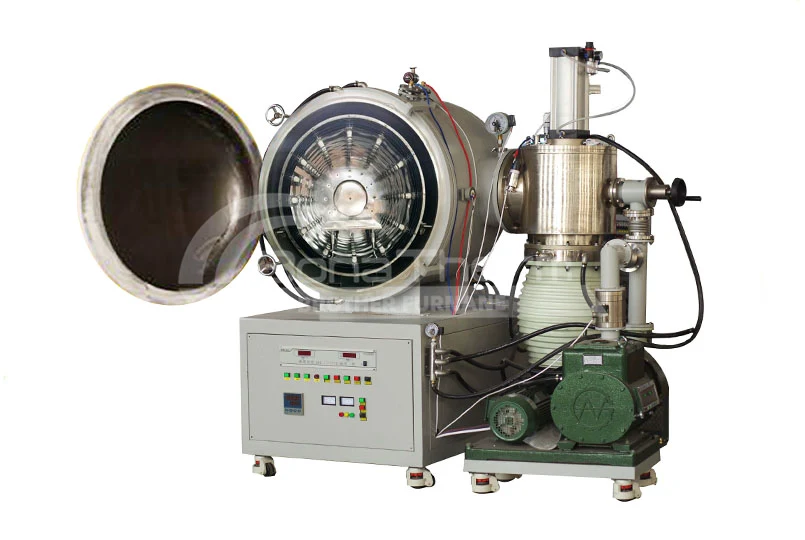
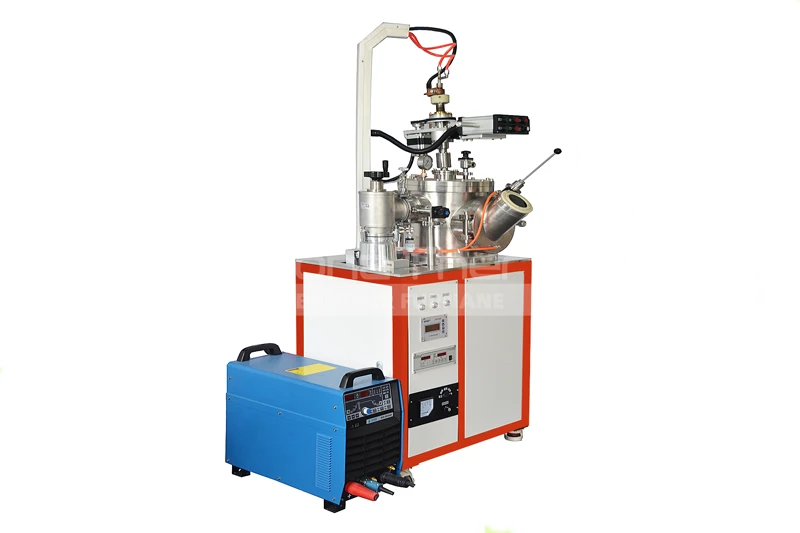
Why is Graphite Used as the Furnace Chamber in Vacuum Furnaces?
Why is Graphite Used as the Furnace Chamber in Vacuum Furnaces?
In modern industrial production, vacuum furnaces have become indispensable across many fields. Selecting the appropriate material for the vacuum furnace chamber is crucial for ensuring its efficient operation. Graphite is frequently chosen as the preferred material for vacuum furnace chambers. This article will delve into the reasons why graphite is used as the furnace chamber material in vacuum furnaces.
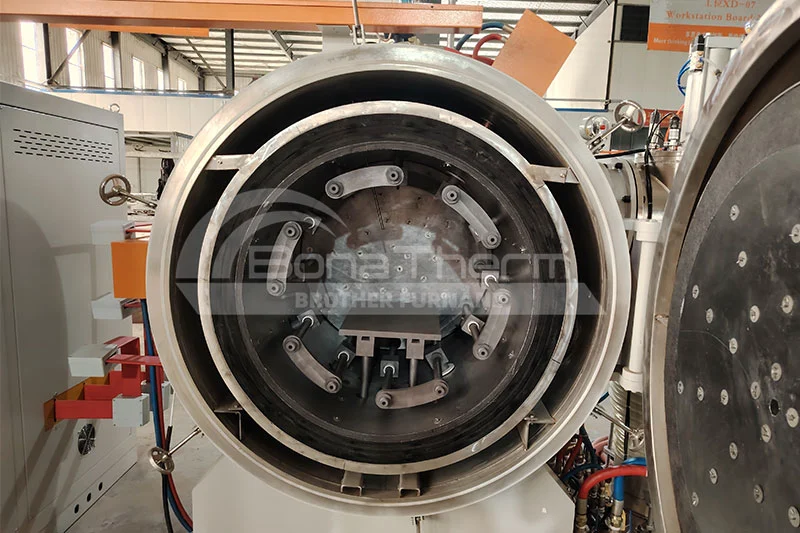

The Advantages of Graphite in High-Temperature Applications
High-Temperature Resistance
Graphite possesses exceptional high-temperature resistance, with a melting point of up to 3652°C. In the high-temperature environment of a vacuum furnace, graphite can maintain stability without softening or melting. This ensures that the graphite vacuum furnace retains its structure and performance even under extreme heat conditions.
Superior Thermal Conductivity
Graphite's thermal conductivity is outstanding, enabling it to quickly and evenly transfer heat. In a vacuum furnace, uniform heat distribution is crucial for the success of heat treatment processes. Using graphite as the furnace chamber material ensures an even temperature throughout the furnace, preventing issues related to localized overheating or underheating that could affect the quality of the workpieces.
Excellent Chemical Stability
In high-temperature and vacuum environments, graphite exhibits excellent chemical stability. It resists most chemical reactions and does not react with the workpieces or other materials. This characteristic ensures the long-term stability and reliability of the graphite chamber, reducing the frequency of maintenance and replacement.
Low Thermal Expansion Coefficient
Graphite has a low thermal expansion coefficient, meaning its volume changes very little with temperature fluctuations. During the frequent heating and cooling cycles in a vacuum furnace, the dimensional stability of the chamber material is crucial. Due to its low thermal expansion coefficient, graphite can maintain its size and shape under extreme temperature variations, ensuring the integrity and sealing of the chamber.
Good Mechanical Strength
Although graphite is relatively brittle, it has sufficient mechanical strength for specific applications in vacuum furnaces. Graphite can retain high strength at elevated temperatures, making it resistant to deformation or damage. This makes it highly effective in high-temperature processing environments.
Ease of Machining
Graphite has excellent machining properties and can be shaped into various complex forms and sizes according to specific requirements. This allows the graphite chamber to be precisely tailored to match the design specifications of the vacuum furnace, ensuring optimal heat treatment performance.
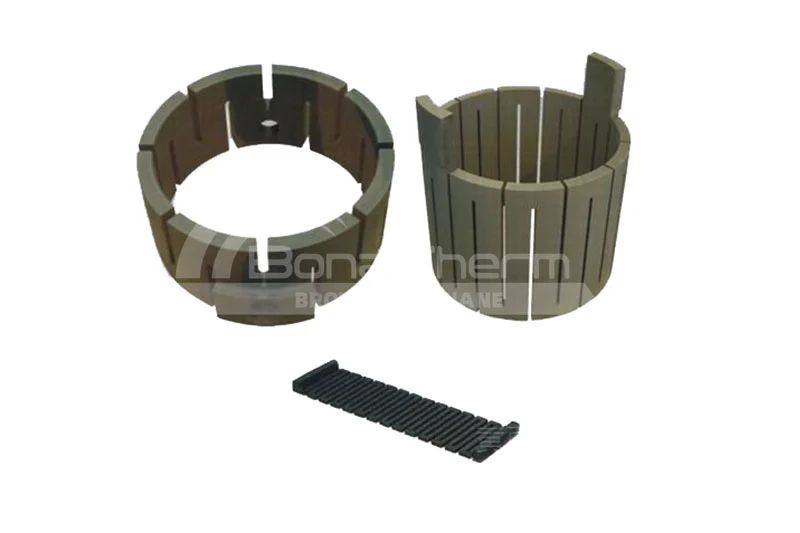

Other Materials for Vacuum Furnace Chambers
In addition to graphite, there are several other materials used for vacuum furnace chambers, such as ceramic fiber, heat-resistant steel, tungsten mesh, and molybdenum foil. Each of these materials has its own advantages and plays a significant role in high-temperature furnace applications.
Conclusion
The choice of graphite as the furnace chamber material in vacuum furnaces ensures efficient, stable, and reliable operation in high-temperature environments. This makes graphite an ideal choice for vacuum furnace chambers and a vital component in modern industrial production.
Brother Furnace has extensive experience in the production of vacuum furnaces. Welcome to consult us.