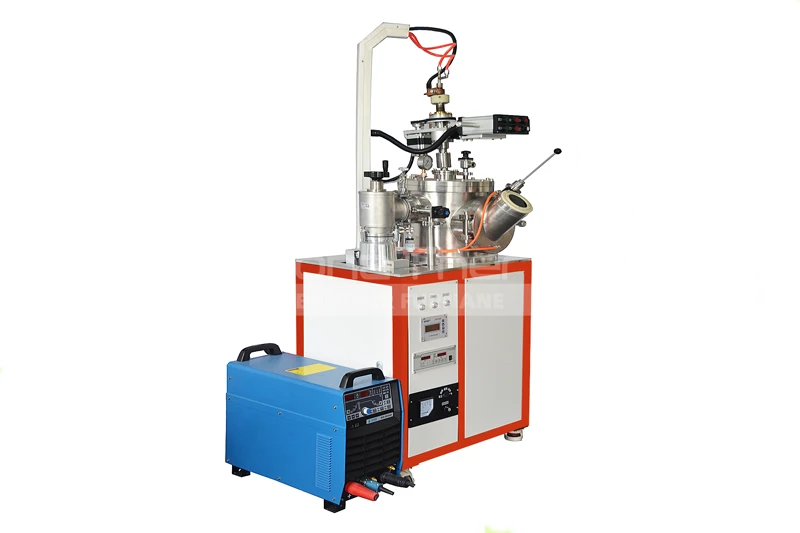
What Are the Types of Vacuum Heat Treatment?
Overview of Vacuum Heat Treatment
Vacuum heat treatment is a series of thermal processes carried out in a vacuum furnace. Reducing or eliminating the presence of oxygen and other gases, prevents oxidation, decarburization, and contamination of materials during heating. This ensures high purity and excellent performance of materials, making it highly valuable in modern industry.
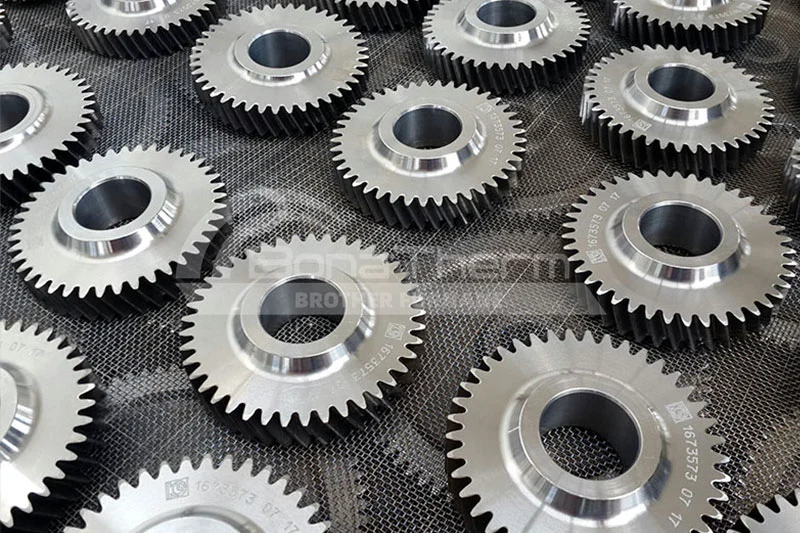

Common Vacuum Heat Treatment Methods
Vacuum Annealing
Application: Mainly used to relieve internal stresses in materials, improving toughness and ductility.
Characteristics: Materials are slowly heated and cooled in a vacuum environment to prevent oxidation and decarburization.
Typical Components: Stainless steel, alloy steel, titanium alloys, and other high-requirement materials.
Vacuum Quenching
Application: Used to increase the hardness and strength of materials.
Characteristics: Materials are heated in a vacuum and then rapidly cooled using gas.
Typical Components: Precision parts, cutting tools, molds, etc.
Vacuum Tempering
Application: Relieves stresses from quenching, improving toughness.
Characteristics: Performed in a vacuum to avoid oxidation and corrosion.
Typical Components: High-strength steels, tool steels, etc.
Vacuum Carburizing
Application: Enhances the surface hardness and wear resistance of low carbon steel and low alloy steel.
Characteristics: Carbon atoms are diffused into the surface of the material in a vacuum, followed by quenching.
Typical Components: Gears, bearings, camshafts, etc.
Vacuum Nitriding
Application: Increases surface hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue strength.
Characteristics: Nitrogen atoms are diffused into the material's surface in a vacuum.
Typical Components: Molds, engine parts, tools, etc.
Vacuum Brazing
Application: Joins different materials, especially those with complex shapes and high precision requirements.
Characteristics: Uses brazing filler metal to join parts in a vacuum, ensuring high strength and excellent joint quality.
Typical Components: Aerospace parts, electronic components, heat exchangers, etc.
Vacuum Sintering
Application: Used in powder metallurgy and ceramic material manufacturing.
Characteristics: Powder materials are heated and sintered into solid form in a vacuum.
Typical Components: Hard alloys, ceramic parts, magnetic materials, etc.
Vacuum Gas Quenching
Application: Cools materials slower to avoid quenching cracks and deformation.
Characteristics: Conducted in a vacuum with controllable cooling rates using gas.
Typical Components: Large-sized parts, complex-shaped components, etc.

Advantages of Vacuum Heat Treatment
No Oxidation or Decarburization
Prevents oxidation and decarburization, maintaining high material purity.
Energy Efficient
Vacuum furnaces typically have excellent insulation properties, reducing energy consumption.
Precise Control
Allows for precise control of temperature and atmosphere, enhancing processing quality.
Environmentally Friendly
No pollutant emissions, meeting environmental regulations.
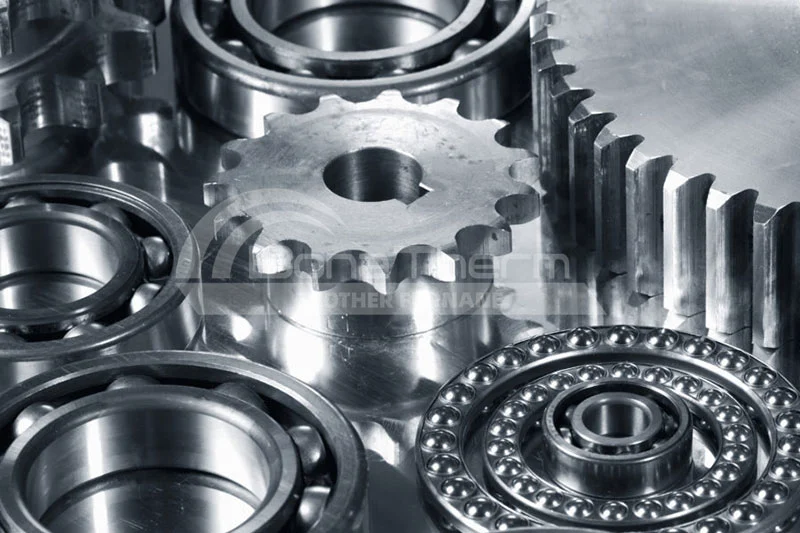
Applications of Vacuum Heat Treatment
Automotive Industry
They are widely used for gears, bearings, and engine parts to enhance wear resistance and lifespan.
Aerospace Industry
They were used for engine components, transmission parts, etc., improving reliability and service life under high-stress conditions.
Machine Tool Manufacturing
Applied to guide rails and fixtures to improve surface hardness and wear resistance, ensuring machine tool precision and longevity.
Construction Machinery
Enhances the wear resistance and service life of transmission parts in machinery like excavators and bulldozers, reducing maintenance costs.

Conclusion
Vacuum heat treatment is an indispensable technology in modern industry, offering performance enhancement and production efficiency through various methods. Mastering vacuum heat treatment techniques can give enterprises a competitive edge in the market. If you have any questions or need further information about vacuum heat treatment, please feel free to contact us.