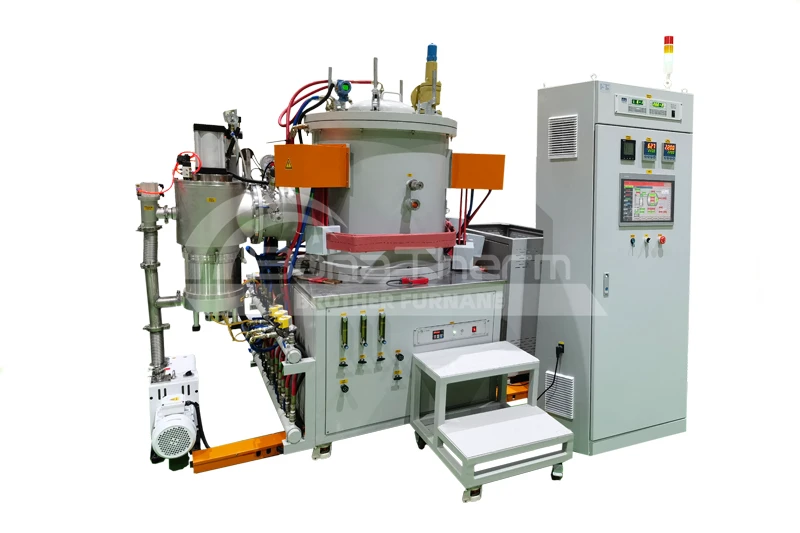
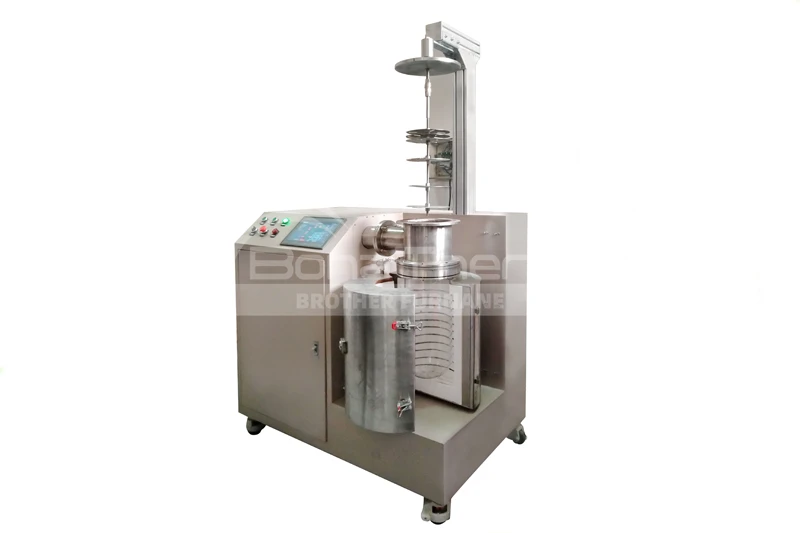
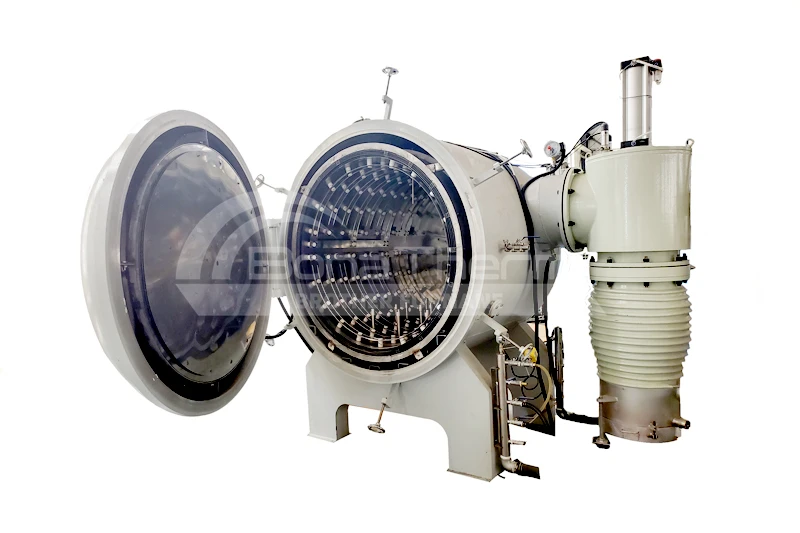
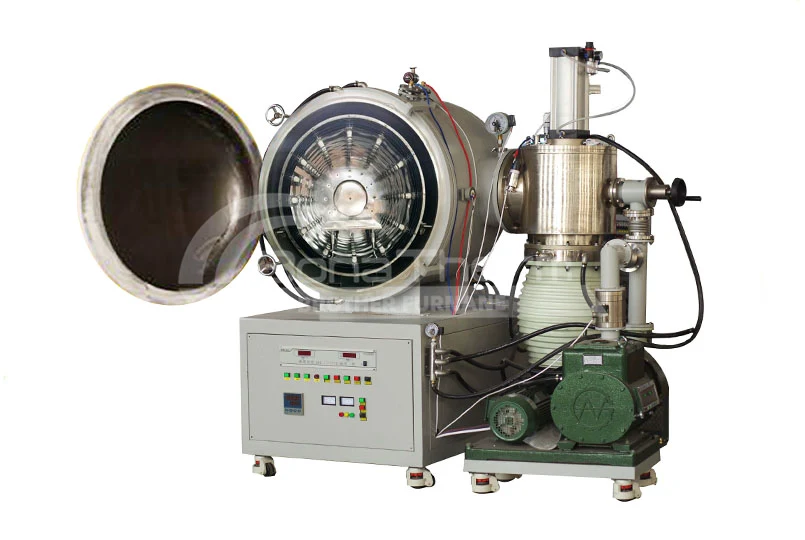
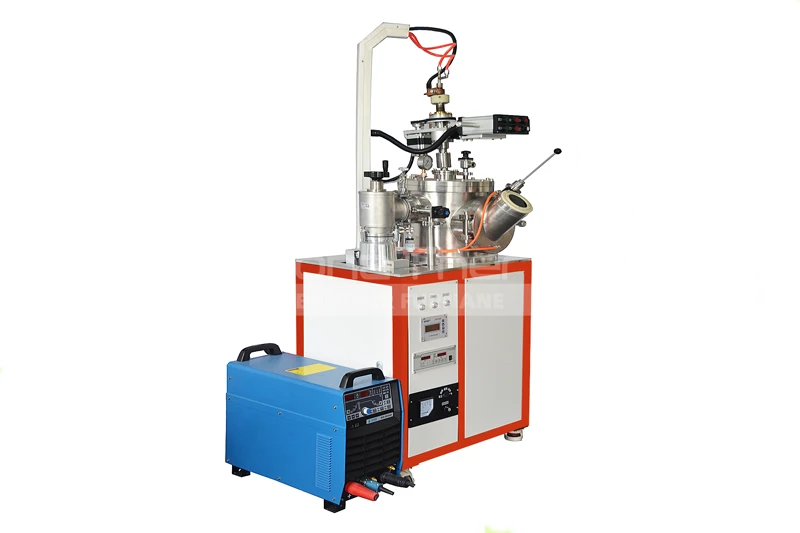
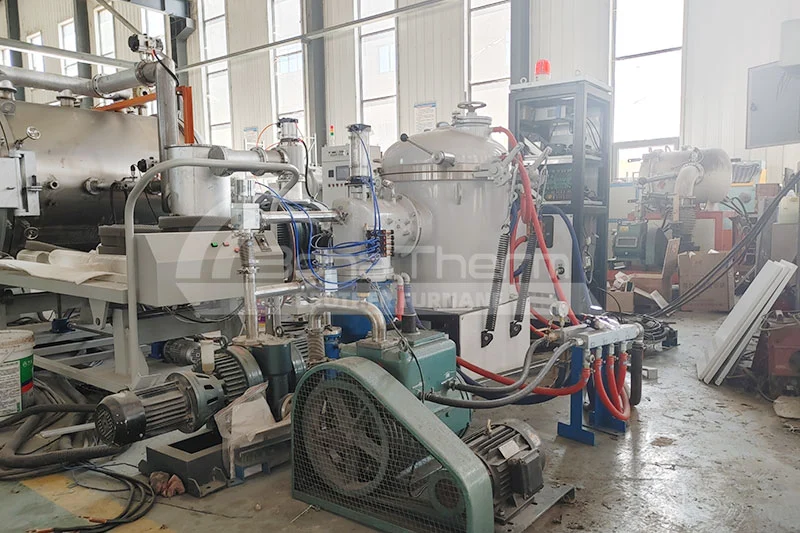
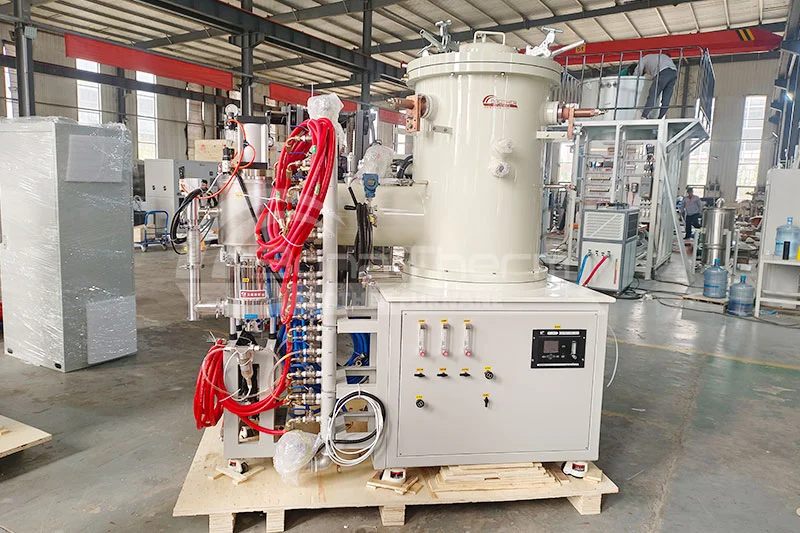
Differences Between Continuous and Batch Vacuum Furnaces
In modern industry, vacuum furnaces are widely used in heat treatment processes. Based on their operational methods, vacuum furnaces are primarily classified into continuous vacuum furnaces and batch vacuum furnaces. Understanding the differences between these two types of vacuum furnaces can help you choose the equipment that best suits your needs. This article will explain the differences between them in terms of working principles, application areas, cost, and energy consumption.
 |  |
Working Principles
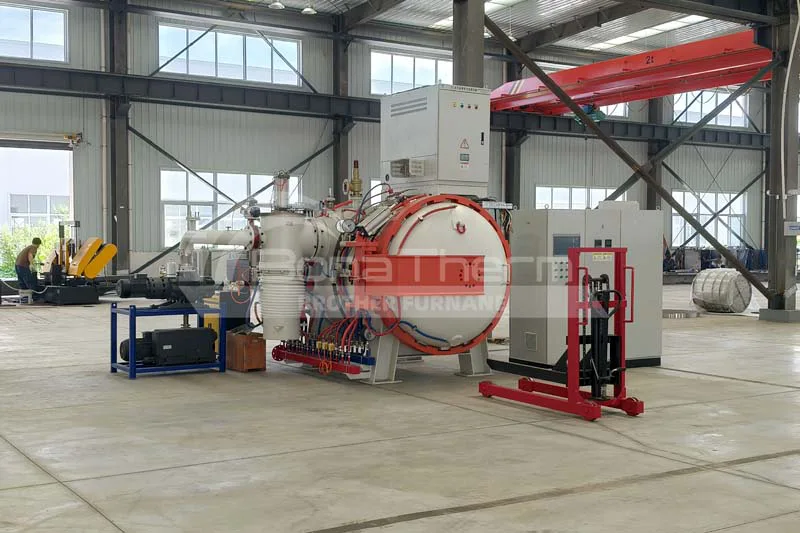
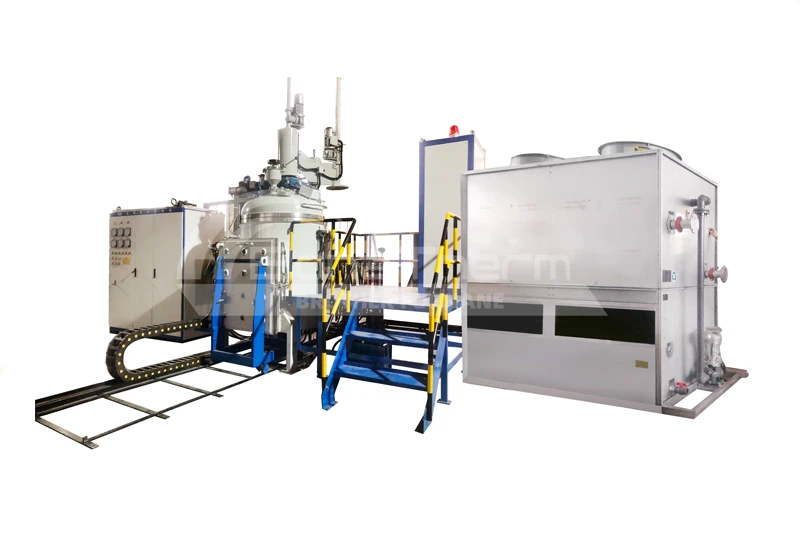
A continuous vacuum furnace utilizes an automated conveyor system to continuously transport workpieces through various processing zones. The workpieces undergo heating, soaking, and cooling sequentially in a vacuum environment, completing the heat treatment process.
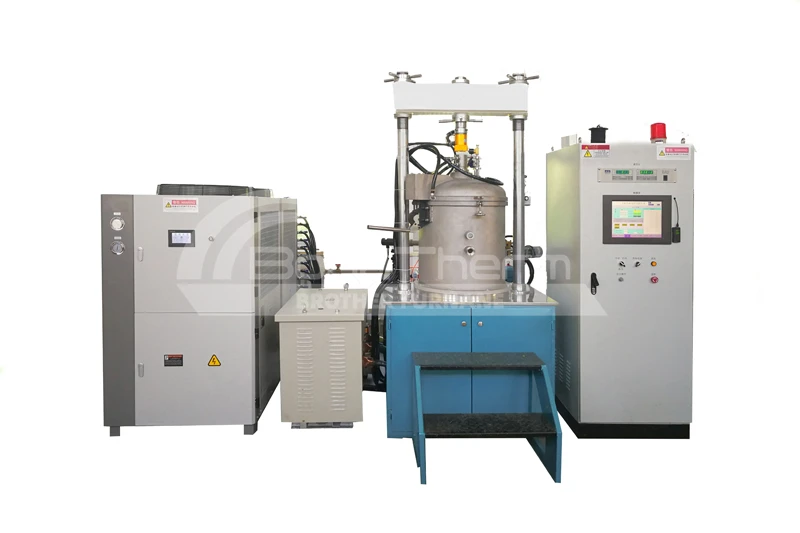
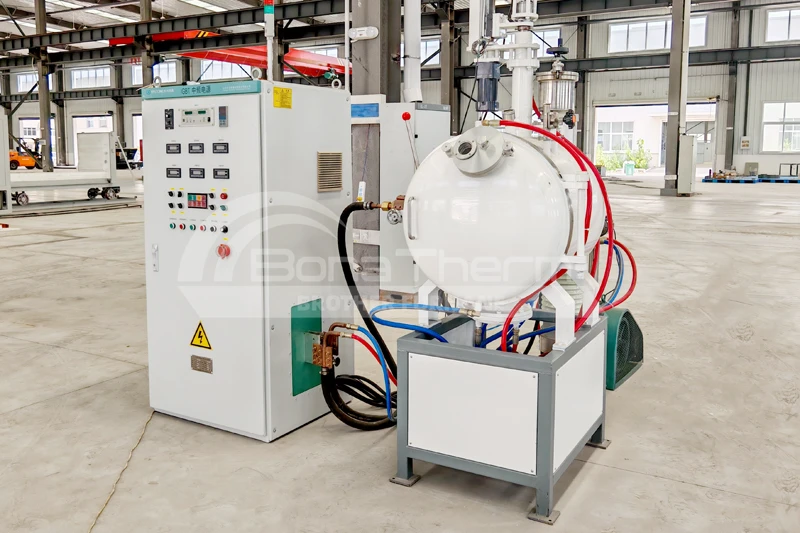
In contrast, a batch vacuum furnace operates by loading a batch of workpieces into the furnace, completing the heating, soaking, and cooling processes, and then removing the treated workpieces. Each processing cycle is conducted independently.
Application Areas
Continuous vacuum furnaces achieve high-volume production through continuous workpiece transfer, making them ideal for high-efficiency production environments.
· Metal Heat Treatment: Used for processes such as hardening, tempering, and annealing.
· Electronics Manufacturing: Employed in the heat treatment of semiconductors and electronic components.
· Aerospace: Suitable for the heat treatment of aerospace materials.
· Automotive Industry: Used for the heat treatment of engine parts, gears, and bearings.
Batch vacuum furnaces are characterized by independent processing of each batch of workpieces, making them suitable for small-batch and multi-variety production needs.
· Laboratory Research: Used for materials research and small-scale trial production.
· Special Component Processing: Suitable for the treatment of high-precision components.
· Small-scale manufacturing: Such as the heat treatment of jewelry and handcrafted items.
Equipment Costs and Energy Consumption
Although continuous vacuum furnaces have higher equipment costs, their high production efficiency can bring significant economic benefits to large enterprises. Conversely, batch vacuum furnaces have lower equipment costs, making them suitable for the budgets of small and medium-sized enterprises while still meeting production needs.
Continuous vacuum furnaces are energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, making them ideal for long-term, large-scale production, helping businesses reduce operational costs. While batch vacuum furnaces have relatively higher energy consumption, their flexibility makes them suitable for short-term and small-scale production tasks.
Conclusion
Choosing the appropriate type of vacuum furnace depends on specific production requirements and application areas. Continuous vacuum furnaces are suited for high-volume, high-efficiency production, whereas batch vacuum furnaces are suitable for small-batch, multi-variety, and high-precision production. By understanding the differences between these two types of vacuum furnaces, you can better select the equipment that meets your business needs, ensuring enhanced production efficiency and product quality.
For more information about vacuum furnaces, please contact us at Brother Furnace.